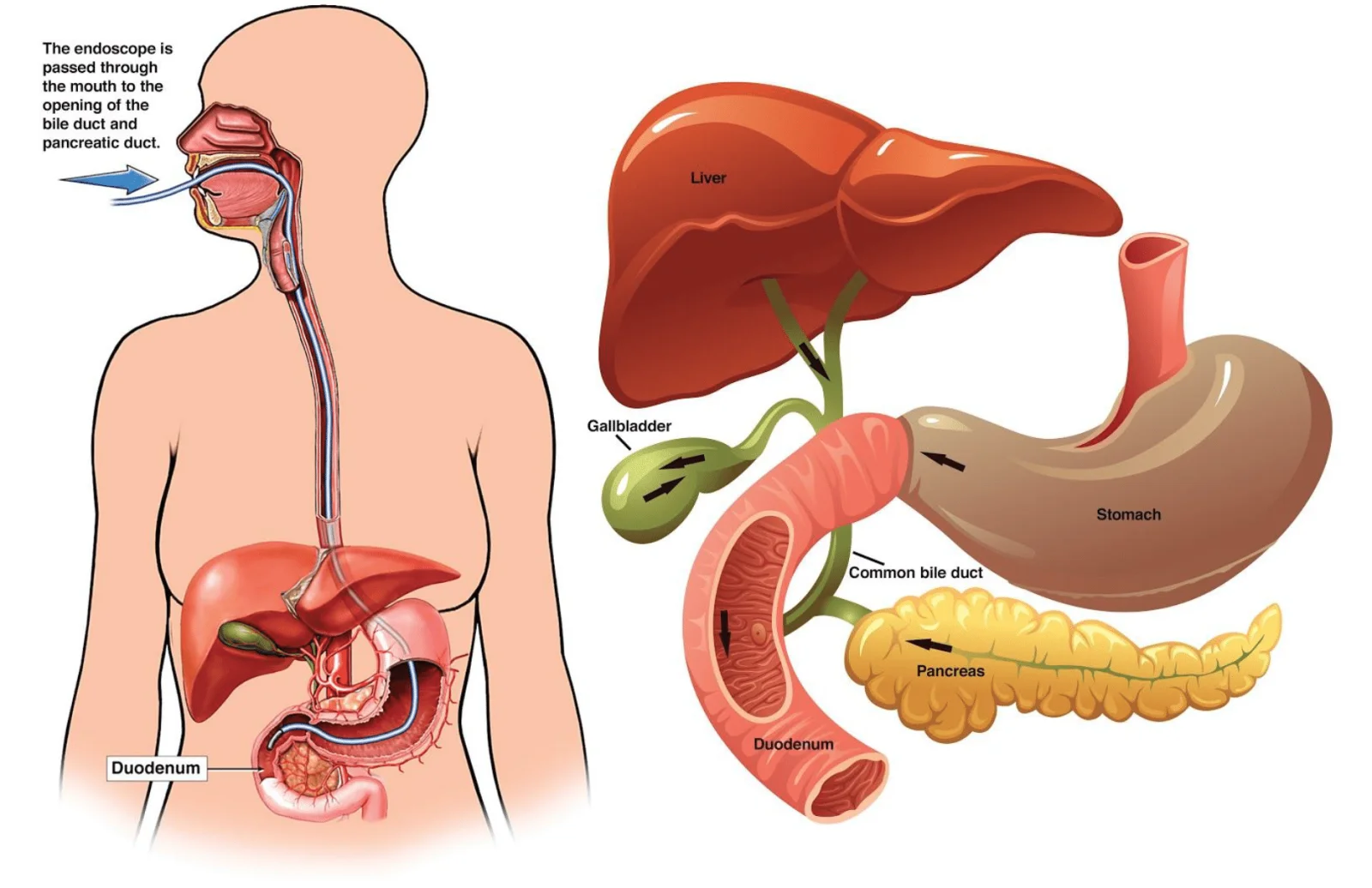
Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) is a specialized technique that combines endoscopy and fluoroscopy to diagnose and treat problems of the bile ducts, gallbladder, and pancreas. It is commonly used to remove bile duct stones, insert stents, or take biopsies. The procedure helps manage conditions such as strictures, tumors, and infections, offering both diagnostic insight and therapeutic relief with minimal invasiveness.
During the procedure, a flexible endoscope is inserted through the mouth into the stomach and duodenum. A contrast dye is then injected into the bile and pancreatic ducts, and X-ray images are taken to visualize and treat abnormalities.
Here are some common questions about ERCP:
No, ERCP is usually performed under sedation or general anesthesia, so patients do not feel pain during the procedure.
ERCP is used to treat bile duct stones, tumors, strictures (narrowing), infections, and leaks in the biliary or pancreatic ducts.
Most patients can go home the same day, although some may require a short hospital stay depending on the complexity of the procedure.